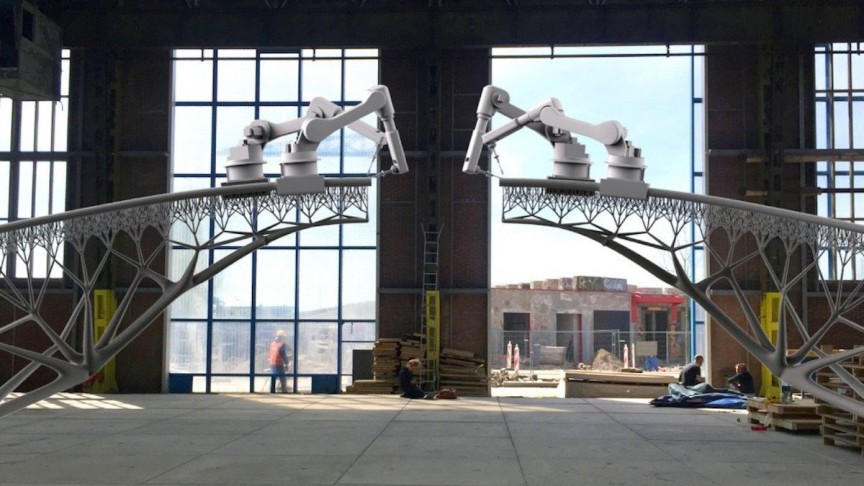
Parametric and Generative designs are innovative approaches to design. Each uses computer software and artificial intelligence to deliver high-quality solutions.
Parametric and generative design represents the future of design. For starters, both rely on advanced algorithms in the process. They also offer speed and reliability and have a broad range of uses – most important being in industrial design and architecture.
Both approaches are much faster than traditional design methods. That makes them perfect for projects with short deadlines. Other than that, they are also suitable for complex projects.
And both parametric design and generative design can work with plenty of data.
Parametric design allows the designer to make changes in real-time. It also allows them to reuse elements and parts in many projects.
Generative design, on the other hand, delivers solutions in iterations. The AI algorithm uses the input metrics to separate good features from the bad. It then uses a scoring feature to make the next iteration.
Constraints and parameters are vital components of both. Parametric and generative design are both highly reliant on the data provided. If the information is not up to par, the software will not be able to deliver the right result.
Here’s a more detailed discussion of the difference between them.
What Is Parametric Design?
Parametric Design is an interactive process. It allows you to create designs based on the input of parameters, such as materials, site constraints, and even environmental issues.
This allows designers and engineers to make changes to the project in real-time because the software will update the model automatically. This approach allows designers to explore many options before deciding on the final design.
The design process relies on computer software and is suitable for a broad range of uses. Architecture and industrial design are only two of them. Also, it’s highly useful in situations where a client needs fast and reliable results. But it still can’t replace designers and engineers.
The input parameters are important in this approach and their accuracy is the key.
Let’s take a closer look at the pros and cons of parametric design.
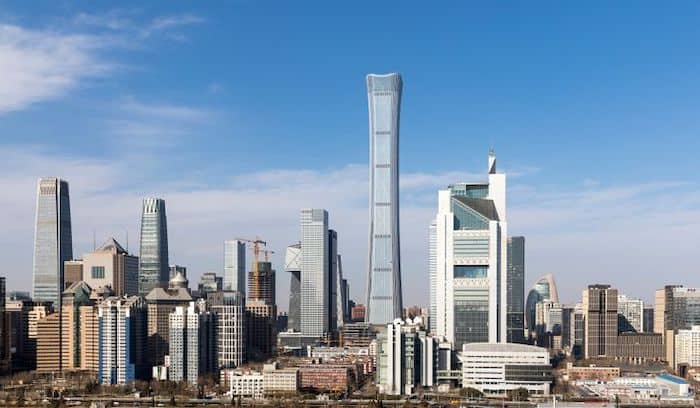

The Pros and Cons of Parametric Design
Pros
Parametric design is much faster than traditional methods. It’s an excellent choice for projects that have a tight deadline. For example, architects used it for the Z15 tower in China. By doing so, it reduced the planning period from weeks to days.
Thanks to parametric design, designers and engineers can now test more solutions than before. That means that they can have more influence on design decisions.
Reusability is another advantage of the parametric approach. If an engineer designs a part that they want to use for several models, they can save it in a matter of seconds. And when they want to work on the next model, they can just import the saved part. This feature of parametric software also allows engineers to share knowledge faster.
Engineers and designers can add constraints to their designs in parametric software. These are particularly important to prevent future design mistakes. And they can also make sure that all modifications follow the original concept.
There exist today specialized programs for a range of industries. Many have a user-friendly interface and are easy to use.
Finally, parametric design uses optimization studies to improve resource efficiency.
Cons
Parametric design also has its flaws. The biggest one is that the set constraints might sometimes clash with each other. That can lead to a less-than-perfect final product. And in the worst-case scenario, the product may be unusable.
Some projects do need strict constraints. But in other cases, design flexibility takes the top spot. If the constraints are too strict, they can slow down the project and increase costs.
What Is Generative Design?
Generative design relies on computers and artificial intelligence. It’s an iterative process that uses advanced algorithms to find the best solution.
First, the designer needs to set constraints and goals. And they also need to provide metrics for rank the results.
When the software delivers the first set of results, it uses these evaluation metrics to rank them. It starts by rejecting all the poor solutions in each category. After that, it creates another set of solutions based on the features with the highest scores.
This approach allows designers to test thousands of options.
Here are the pros and cons of generative design.
The Pros and Cons of Generative Design
Pros
Generative design software uses artificial intelligence to create solutions. And these are all based on the parameters provided by the designer.
With the built-in AI, the software learns from every set of solutions. This ensures higher-quality future sets.
This design is also much faster than the standard process. It allows designers and engineers to explore a broad range of solutions in a short amount of time. That’s because the software makes many decisions for the designer.
Generative design can also lower risks associated with the project. If it gets the right parameters, the algorithm can understand complex data. It can also predict the risks and dangers. Architecture can include information about the weather in its calculations.
Cons
Generative design also comes with drawbacks, though not necessarily of its own doing. The biggest is its potential to automate many jobs and make human workers redundant. That’s especially true in the construction industry. Wood trades, painters, plasterers, floorers, and decorators are also vulnerable to automation.
In fact, a Mace study claims that AI will replace many construction workers by 2040. And it also predicts great job losses in other industries.
Beyond potential industry concerns, generative design still requires human interaction. A design created using this technology is only as good as the initial brief that the designer creates. Should the designer not understand how to utilise AI, generative design may produce poor results for them.
Furthermore, generative design often requires large amounts of computational power. While this issue is mitigated, it is still a concern and will continue to be so, depending on the developments in cloud technology.
Future of Design
Parametric and generative designs are the future. Both methods offer reliable performance and speed. And they also allow designers to test many solutions.
In addition, parametric and generative design can lower project costs by a large margin. For that, both would require precise data and a deeper understanding of the technologies, which will come with time.
Perhaps the biggest benefit of both technologies is their use of AI. While some see increased AI use as a threat, the reality is that AI is simply a tool. AI still needs the output of people.
When people harness AI correctly, it allows for enormous productivity increases. This results in the faster creation of designs. Not only that, this enables even small firms to take on more work.
In short, AI and human intervention exponentially multiplies output.
If you want to find out more about generative design and how it works, you should check out Archistar. It’s the software platform of choice for many property developers. The features include assessment, 3D modelling, and generative building design. To experience Archistar’s full power, Get started for free: [https://www.archistar.ai/]